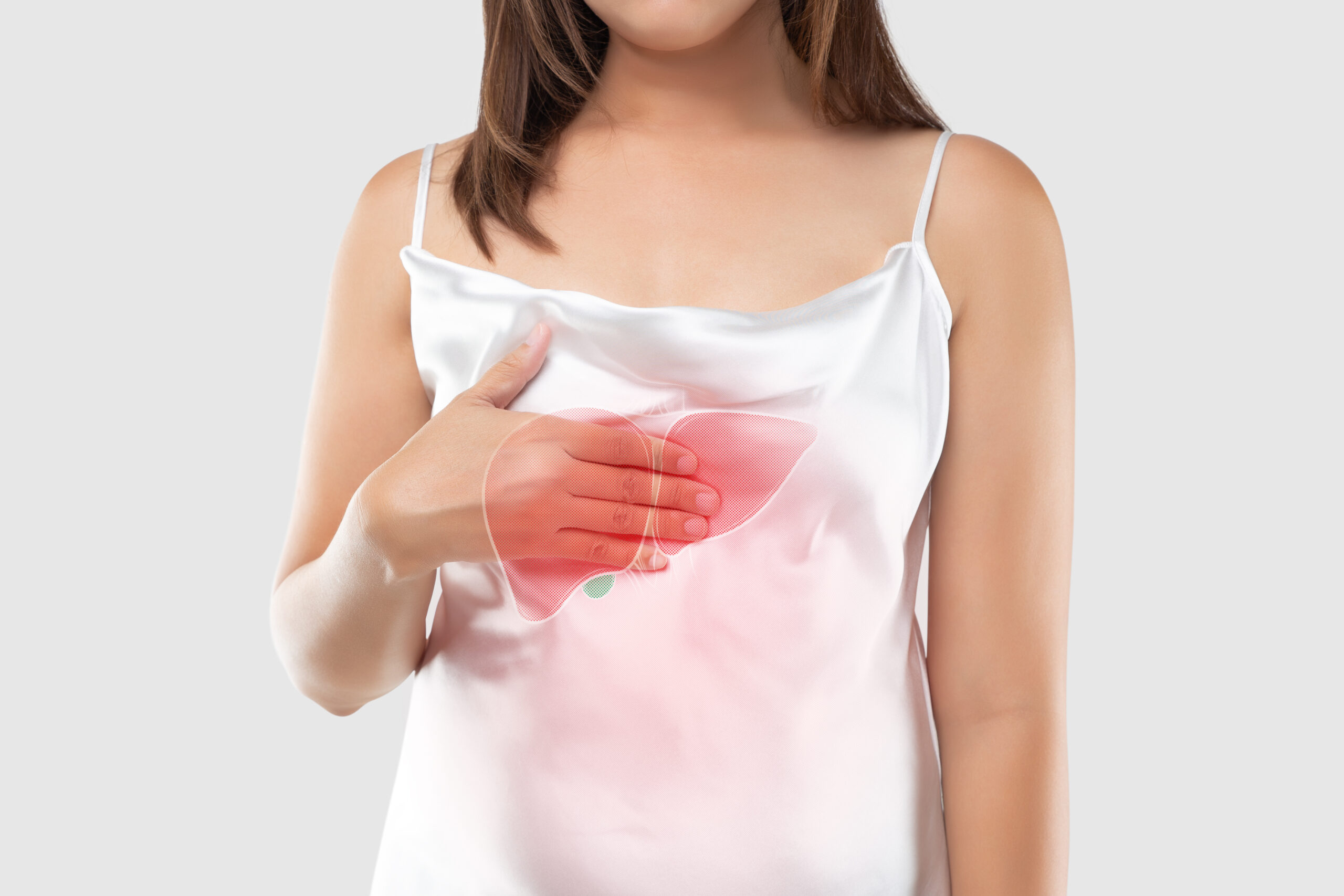
Pancreatic cancer is responsible for seven percent of all cancer-related deaths in the country. It is a disease of the pancreas, a small organ located in the abdomen that helps convert food into fuel for the body’s cells. When the pancreas is affected by cancer, it cannot function normally. The cancerous cells keep multiplying and develop into a tumor.
What causes these cancerous cells to grow in the pancreas remains unknown. While inherited genes can develop mutations and lead to pancreatic cancer, the number of such cases is relatively small. So to think that pancreatic cancer is a hereditary disorder isn’t totally accurate. Various other factors have just as big a say.
Risk factors for pancreatic cancer
Besides specific genetic mutations, such as mutations in the gene PRSS1 (familial pancreatitis) and gene NF1 (neurofibromatosis, type 1), a host of other factors can also increase the risk of pancreatic cancer. The most significant risk factors include the following:
- Age
Adults of any age can develop pancreatic cancer, although the risk increases significantly for those who are 45 or older. Individuals over the age of 55 are even more likely to develop the condition. - Gender
Data suggests that men are more likely to develop and die from pancreatic cancer than women. Estimates from last year point that of the 57,600 adults diagnosed with pancreatic cancer, 30,400 were men. - Diabetes
Pancreatic cancer and diabetes are closely linked. Individuals who have had diabetes for more than five years are the most vulnerable to developing the condition. Sometimes, the onset of type 3c diabetes can also indicate something’s up with the pancreas, and it can be used in the early diagnosis of pancreatic cancer.
Rare inherited diseases
Certain diseases that are passed down from parents can lead to pancreatic cancer. Hereditary pancreatitis (HP), Lynch syndrome, and Li-Fraumeni syndrome (LFS) are a few such disorders known to increase the condition’s risk.
- Obesity
A body mass index (BMI) of 30 or more is a sign of obesity. The condition is known to increase the risk of diabetes and heart disease, in addition to pancreatic cancer. According to statistics, obese individuals are 20 percent more likely to develop pancreatic cancer than those without the problem. - Lifestyle decisions
Poor diet, which is responsible for obesity, has a significant impact on whether an individual will be diagnosed with pancreatic cancer. Foods rich in trans and saturated fats are harmful, and regular consumption of such foods significantly increases the risk of the condition. Alcohol is just as big a problem as it causes recurrent pancreatitis, a disease that causes inflammation of the pancreas. Similarly, people who smoke are two to three times more likely to suffer from pancreatic cancer.