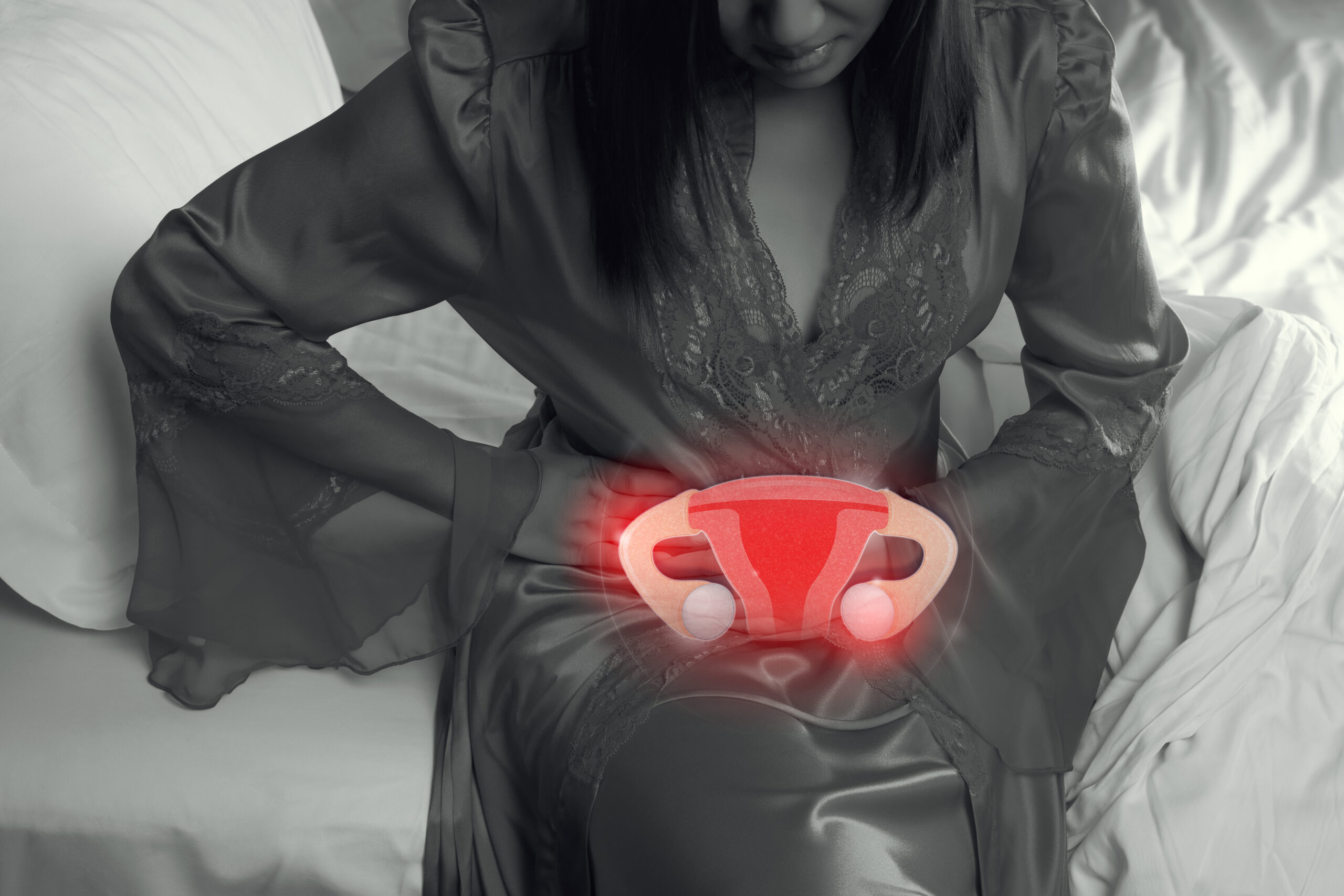
Ovarian cancer is when cancerous growths start developing in cells present in and around the ovaries and the fallopian tubes. Several different types of ovarian cancers are observed in women based on the types of cells or tissues affected and where they begin metastasizing. Certain factors, however, put women at a greater risk of developing ovarian cancer.
Risk factors
- Genetics
Someone with a family history of cancer, specifically ovarian cancer, is more at risk of developing ovarian cancer herself. More people in the family with a history of some cancer further increases the risk of developing ovarian cancer. - Age
In most types of cancers, the risk of developing such growth increases with age. As a result, people over the age of 50 are more likely to be diagnosed with such cancers than those who are younger. This is also true for ovarian cancer in women, especially if they have already been through menopause. - Obesity
It has been observed that women who are slightly overweight or even obese are more susceptible to ovarian cancer. It is also quite difficult for such women to successfully deal with the symptoms of ovarian cancer. Hence it is recommended for women, especially over the age of 50, to lead an overall healthy lifestyle. - Hormonal imbalances
The natural hormonal balance in our body can get disrupted drastically due to external or internal changes such as stress, taking hormone therapy after menopause, or taking contraceptives. This imbalance of hormones can increase the risk of developing ovarian cancer in women. - Treatment options
The treatment options recommended for patients with ovarian cancer can either be surgical or associated with chemotherapy along with other therapy options to accompany. - Surgery
The doctor may recommend getting a surgery done to remove either one or both the ovaries for women with ovarian cancer. It may even be recommended that the patient also get their uterus surgically removed in some severe cases. If the cancer is quite advanced, the doctor will also suggest going through chemotherapy after surgery. - Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy on its own would be recommended only to those patients who are showing very benign cancerous growths. Most of the time, chemotherapy is recommended as a repetitive procedure to be done for some time after surgery is done. - Other treatment options
Along with surgery and chemotherapy, other treatment options can be considered to ensure that the cancer is eliminated from the body for good. Treatments such as targeted therapy and palliative care are often recommended to patients after surgery.