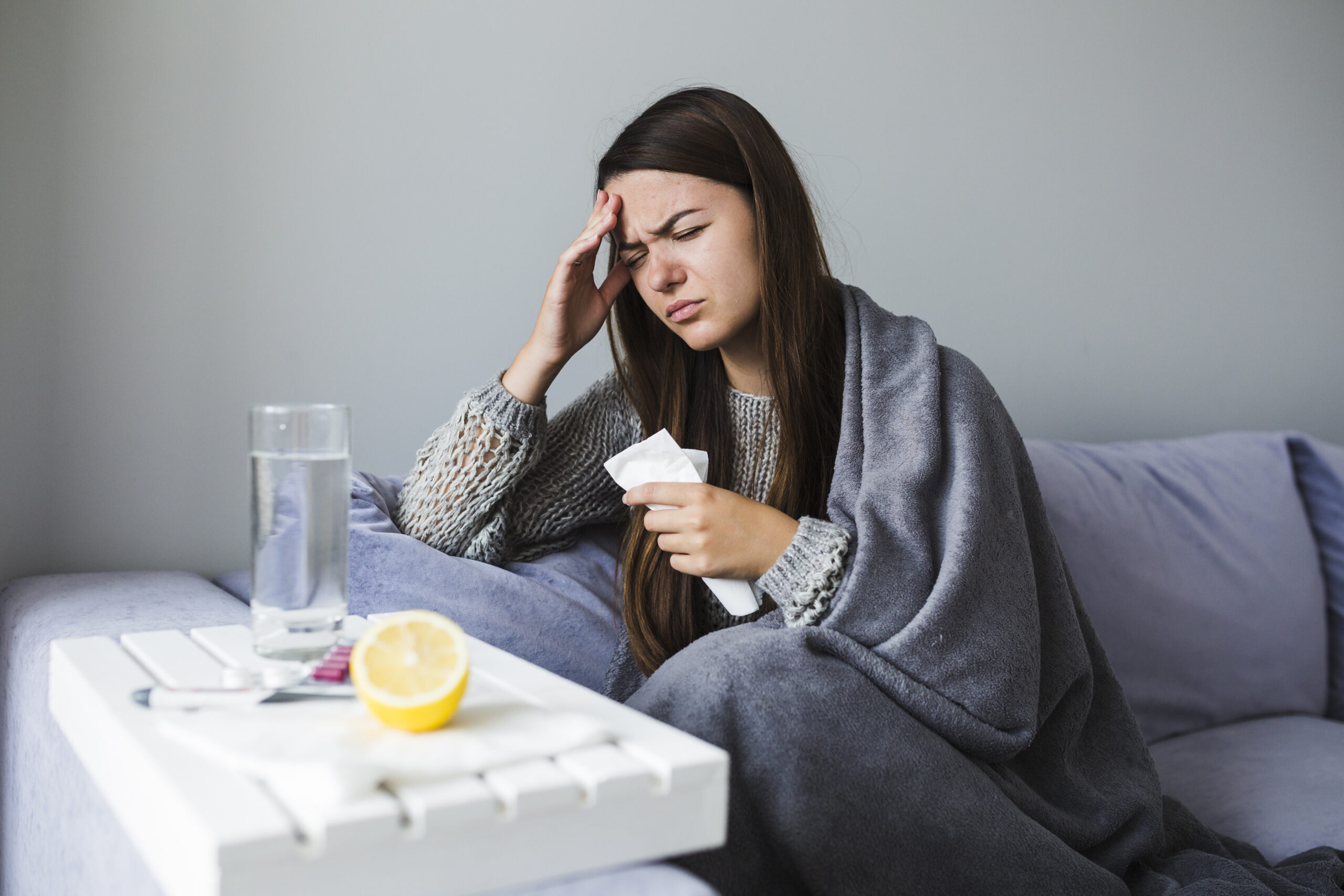
Cold and flu are unavoidable. The pathogens responsible for these illnesses are everywhere, so there’s no “safe place” as such. Fortunately, both problems can be easily tackled and don’t necessarily require medical attention, unless it’s an emergency. The food you eat has the necessary nutrients to dilute the effect of the pathogens responsible for both illnesses. This article takes you through the most effective of these nutrients.
Zinc
Zinc is an incredible mineral that boosts your immune system and helps heal wounds. It proves especially useful against colds; preventing rhinovirus, which is responsible for it, from multiplying or entering the mucous membranes of the throat and nose. Zinc’s antiviral properties make it effective against other types of viruses as well, including the ones that lead to flu. Experts recommend around 8mg of zinc a day for women and 11mg for men. Nuts, beans, and whole grains are the best sources of the nutrient.
Vitamin A
Among the most beneficial nutrients out there, vitamin A promotes growth and development and enhances the function of the immune system. It plays a central role in cellular immune response, also proving effective against infectious diseases such as cold and flu. Its anti-inflammatory properties assist the immune system to carry out its functions effectively. The wider benefits of vitamin A cannot be ignored either, with the micronutrient supporting good vision and reducing the risk of certain cancers.
Vitamin C
Vitamin C is renowned for its wide range of health benefits. As far as its effect on the immune system is concerned, the micronutrient promotes the formation of antibodies, which help in destroying bacteria and viruses. The pathogens responsible for cold and flu are rendered ineffective in this way, while the nutrient also promotes wound healing by increasing the production of collagen. Besides citrus fruits, strawberries, broccoli, and tomatoes are some of the best sources of vitamin C.
Vitamin E
Studies have found that vitamin E supplements might help reduce the risk of common cold. Vitamin E, as a natural antioxidant, enhances the immune system response, which increases immunity and provides better protection against pathogens. It also shields the immune cells themselves, thus increasing their resistance to pathogens. Vitamin E, additionally, maintains skin health and decreases inflammation throughout the body. Almonds, spinach, and vegetable oils are all rich in this nutrient.
Protein
Every cell relies on protein for its overall development. This includes the cells in the immune system, which need protein to repair tissue and prepare themselves for the next wave of bacterial and viral attacks. Meanwhile, the lack of protein in the body weakens the immune system, making it easy for viruses to compromise the body. Lean sources of protein, such as skinless chicken, lean beef and turkey, must be added to the diet to prevent this outcome.